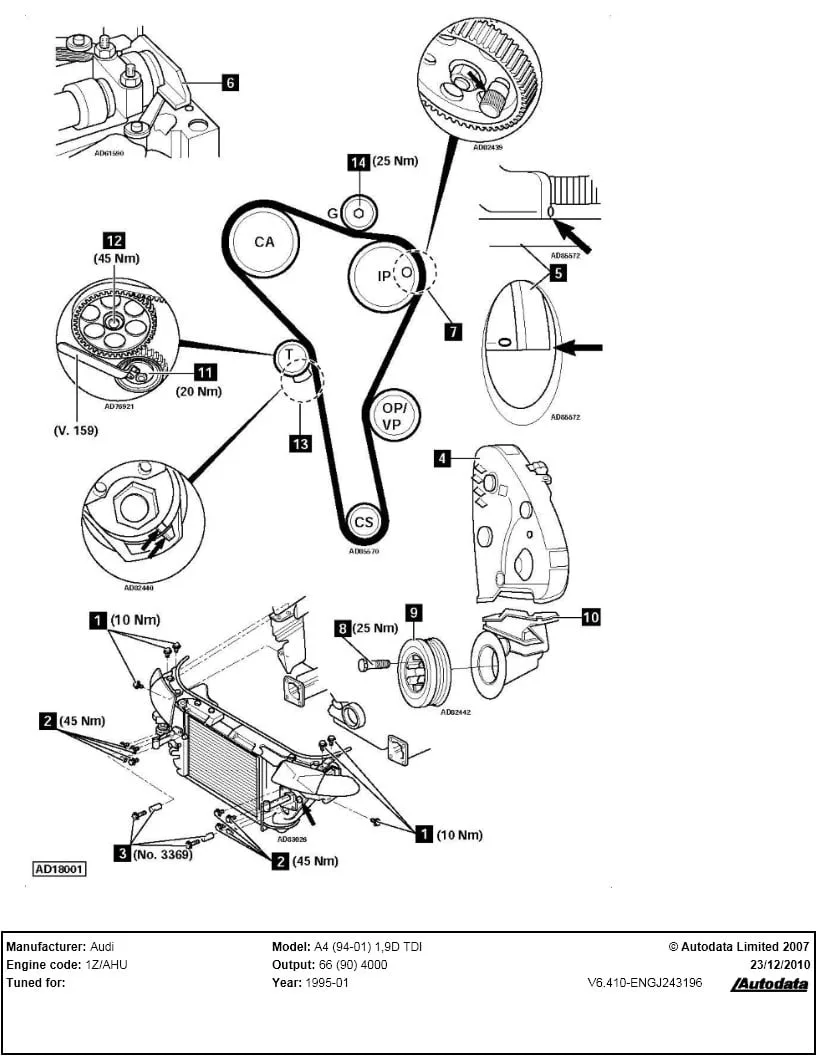
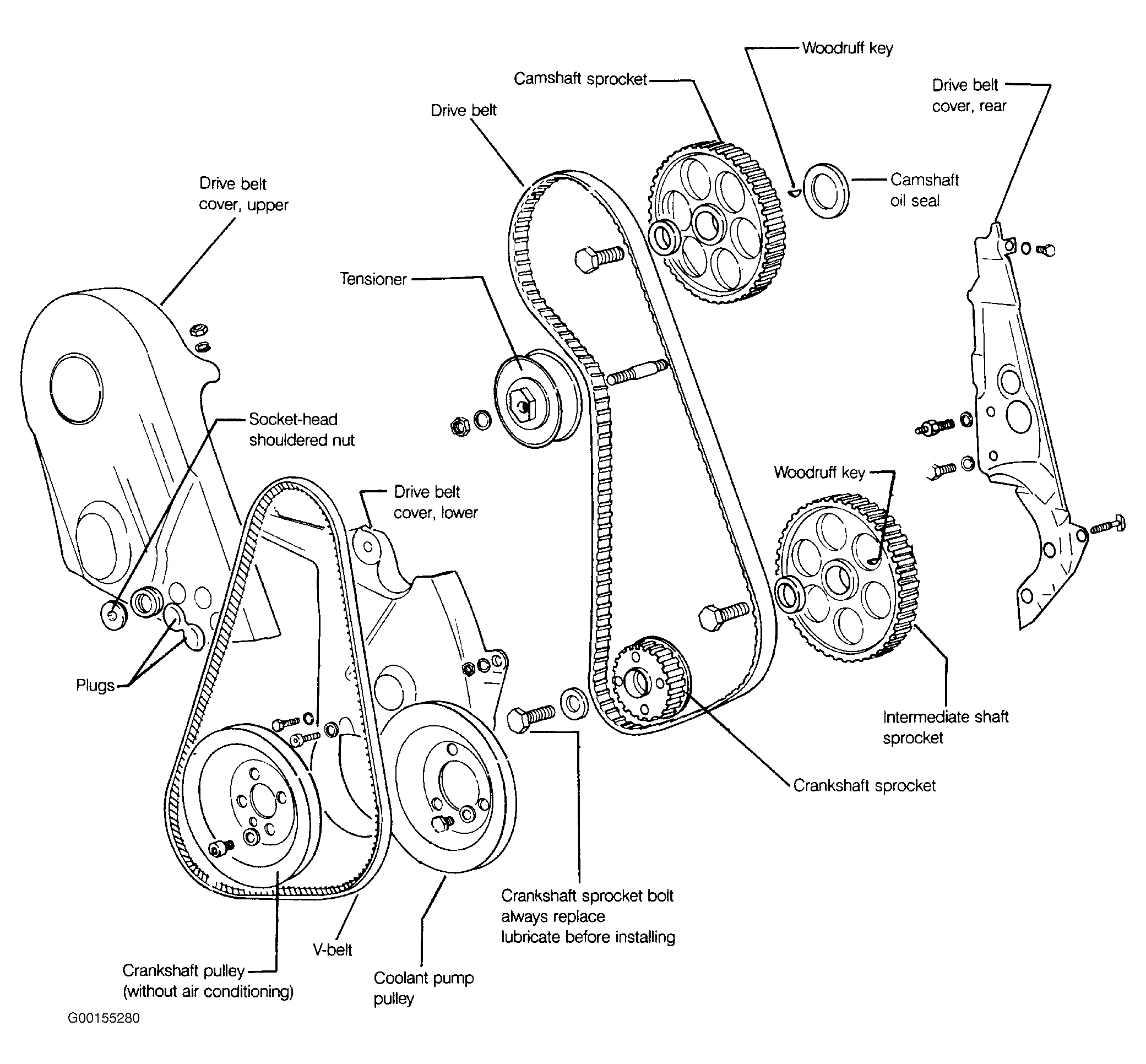
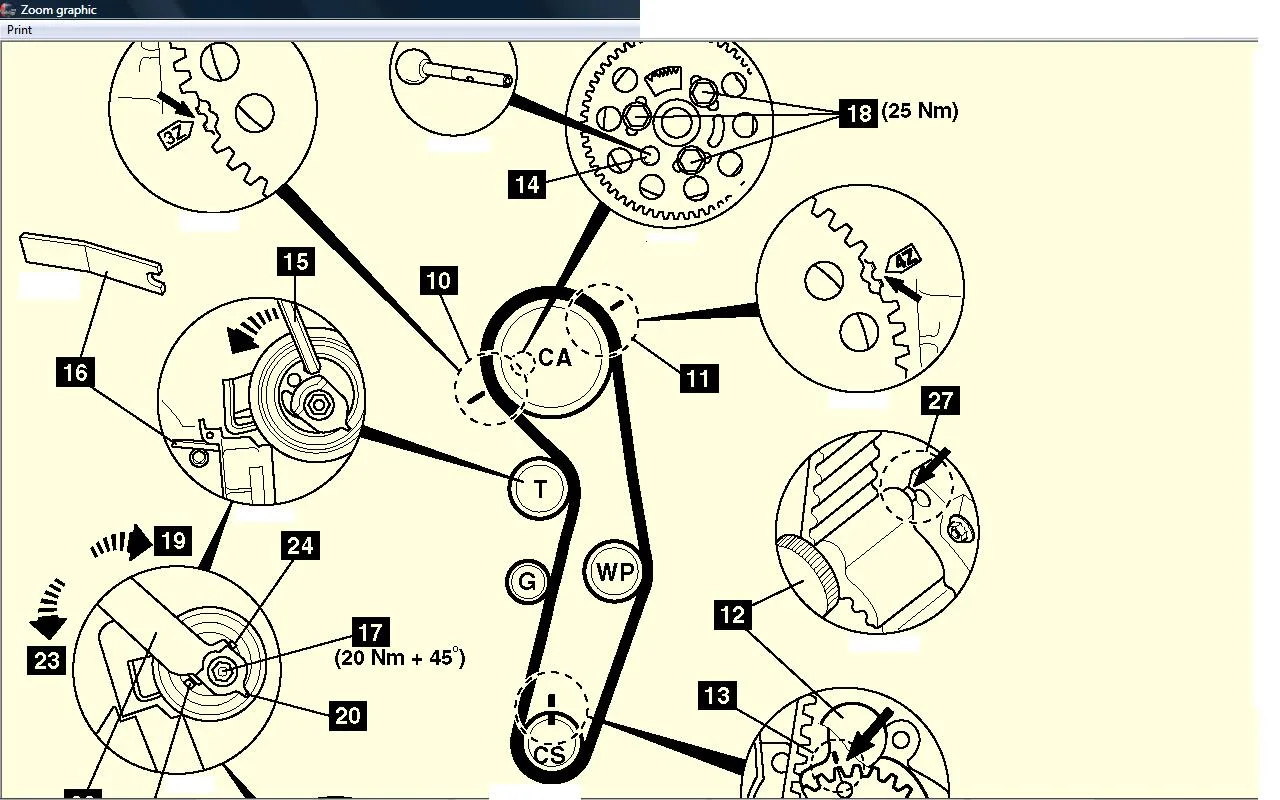
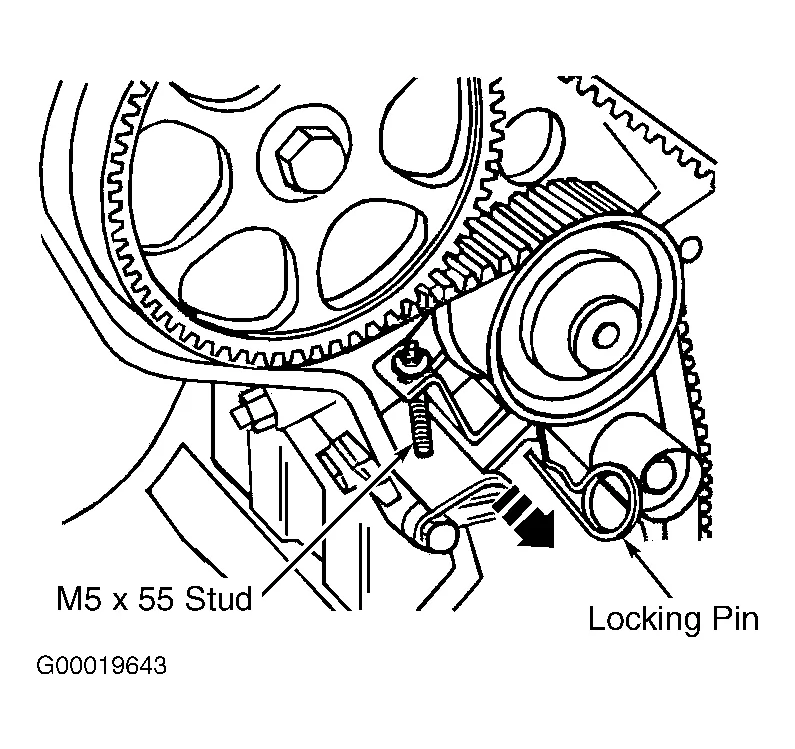
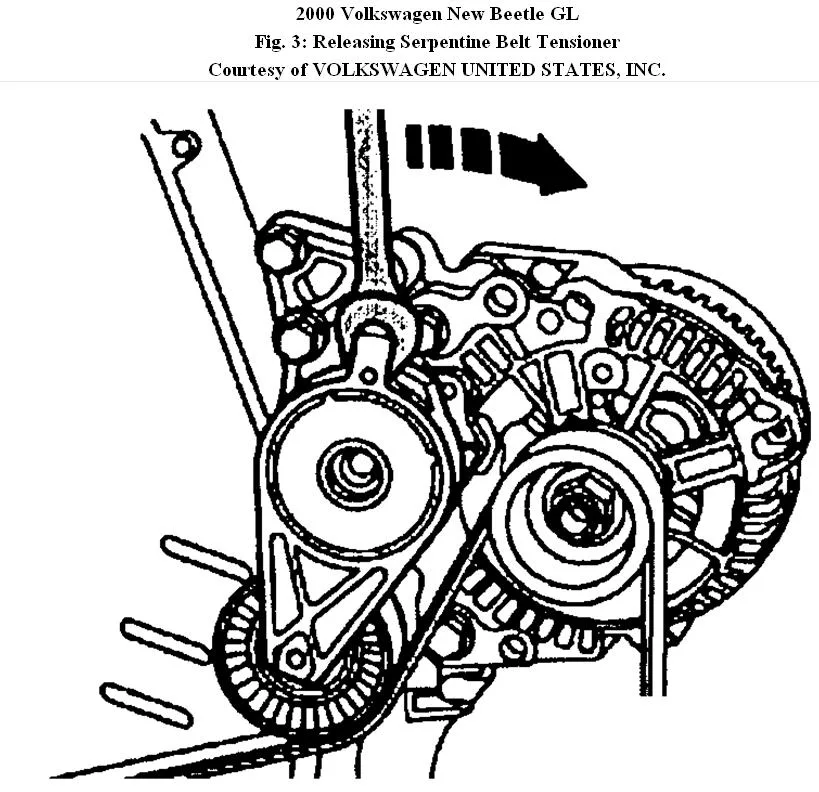
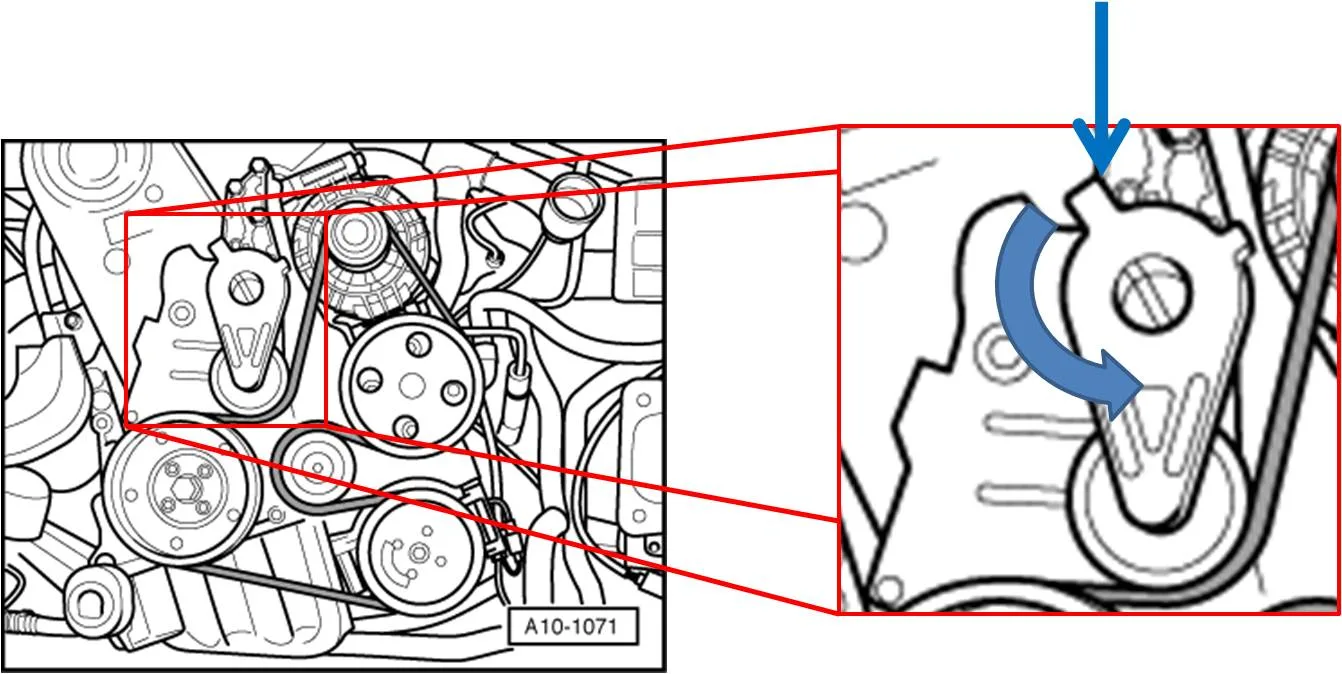
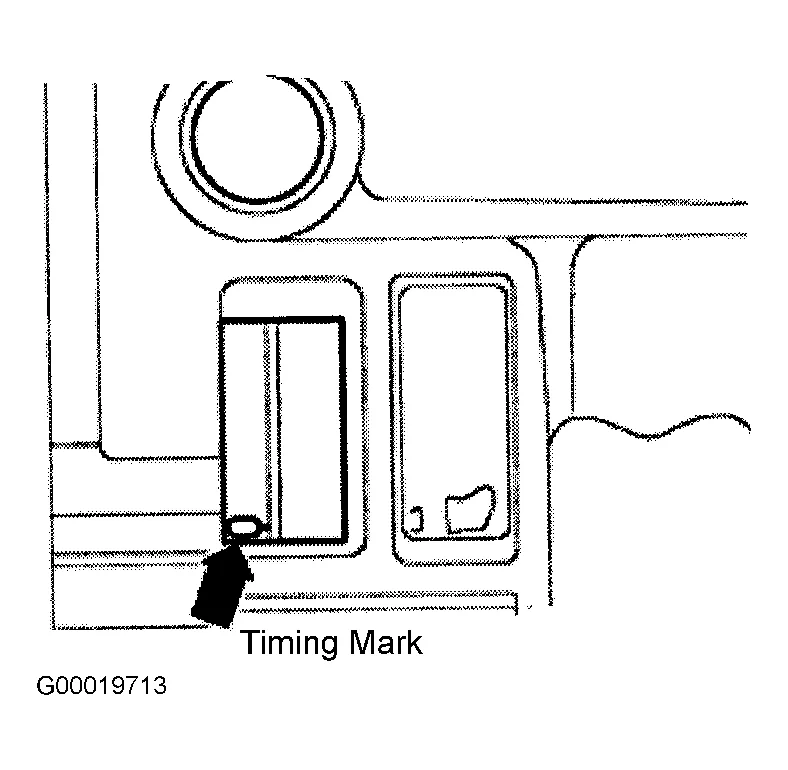
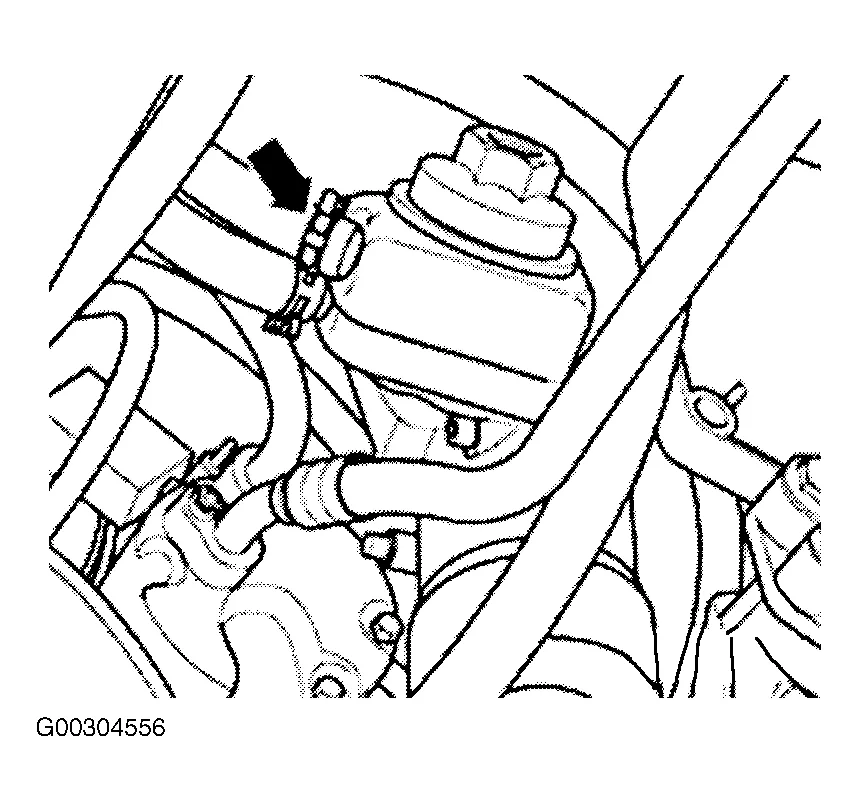
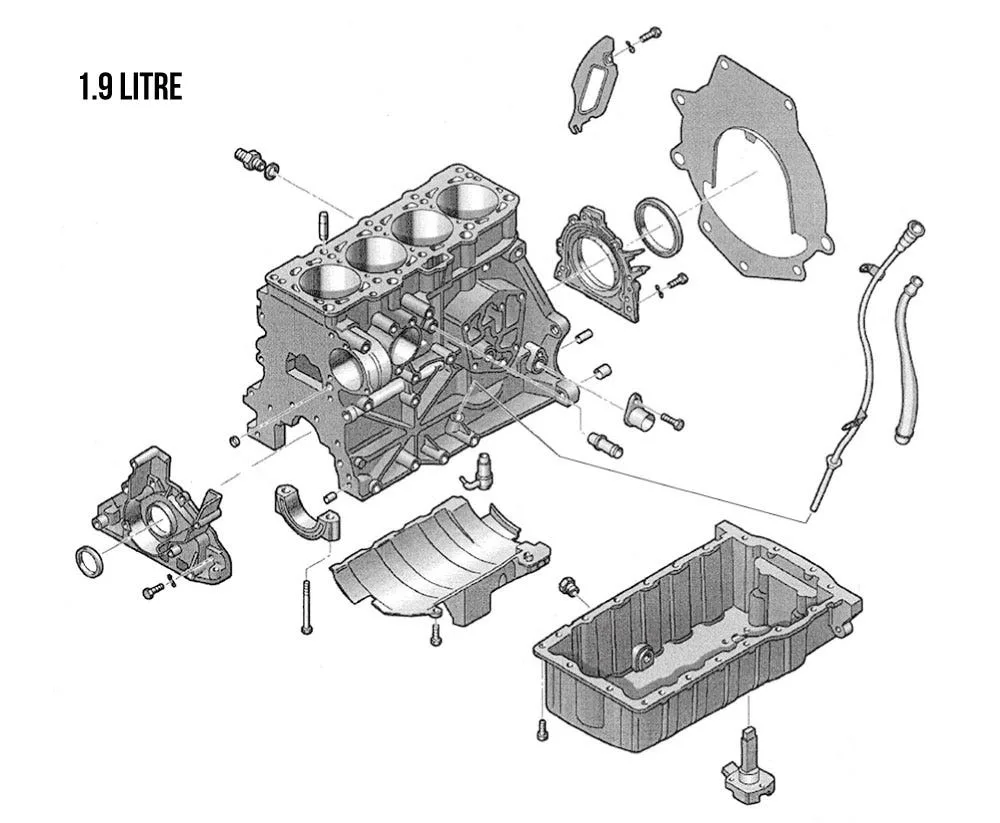
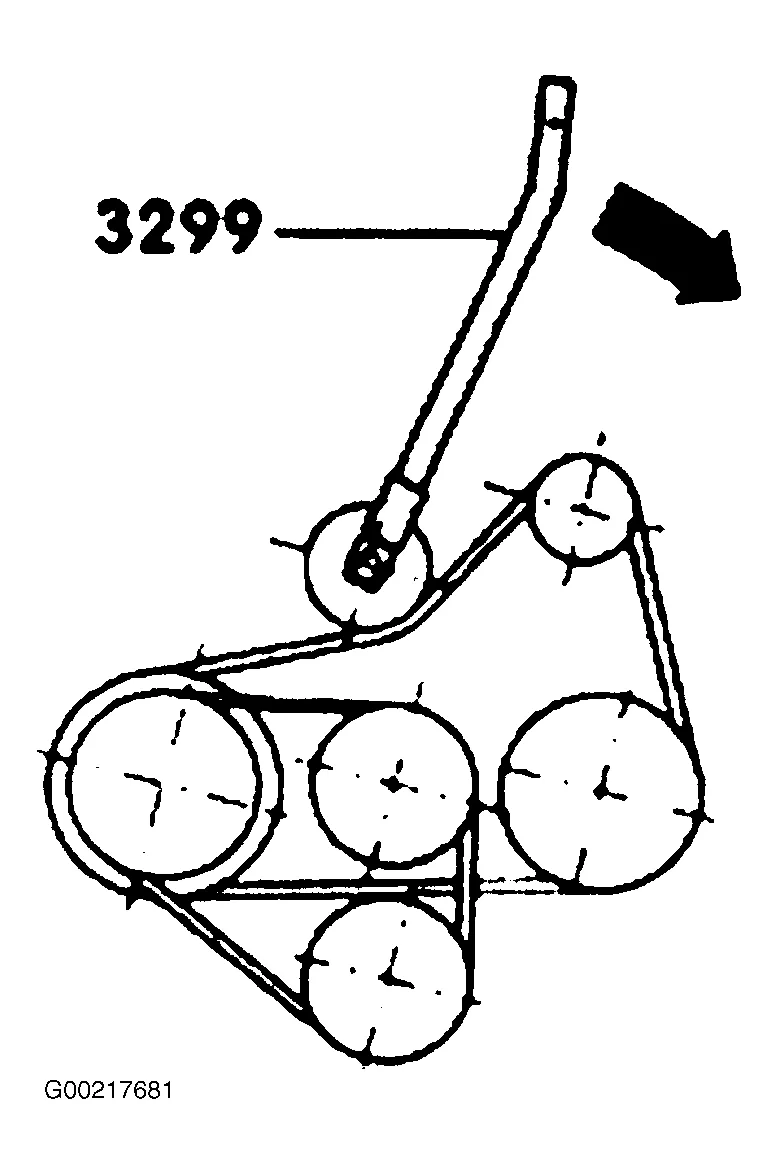
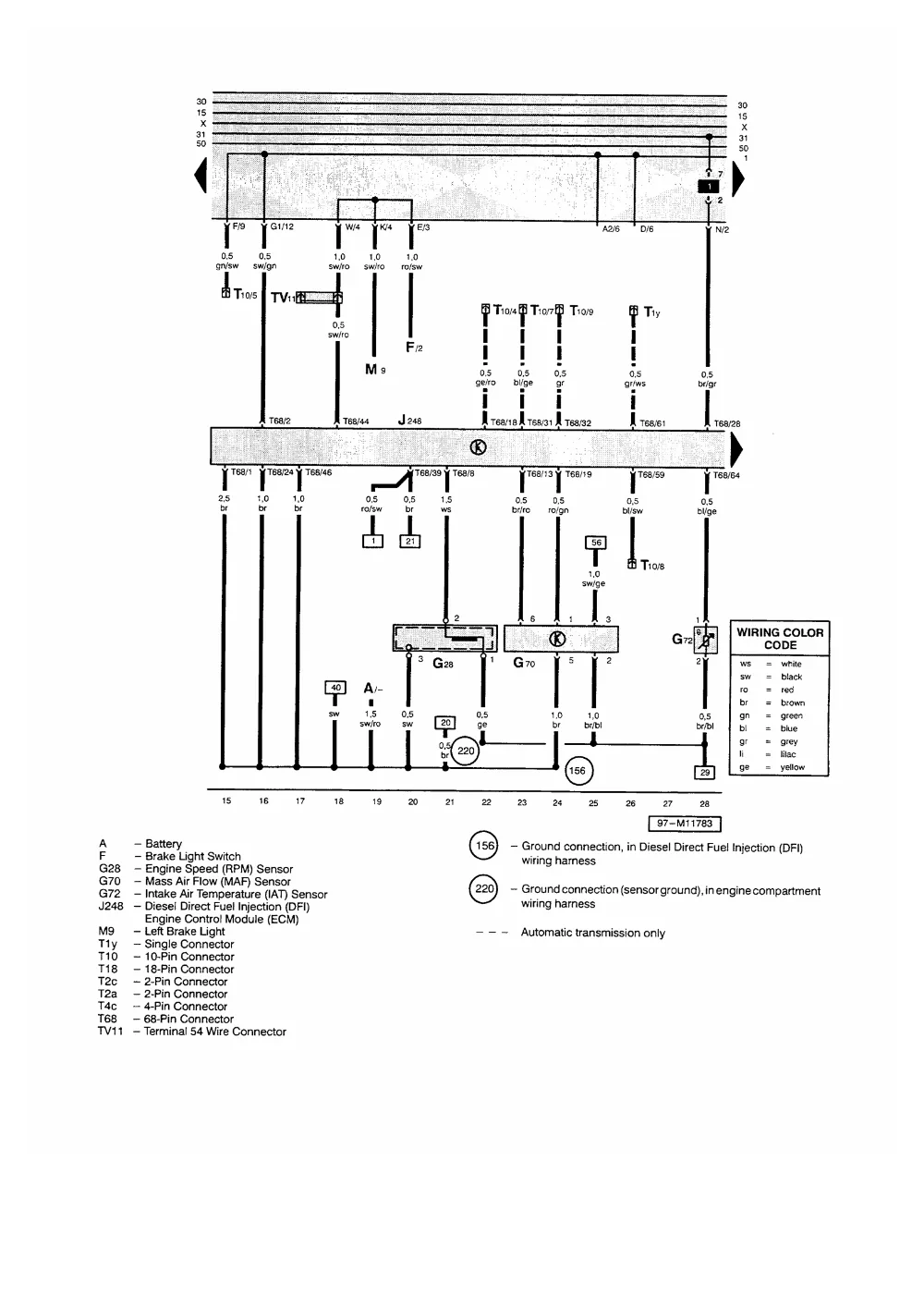
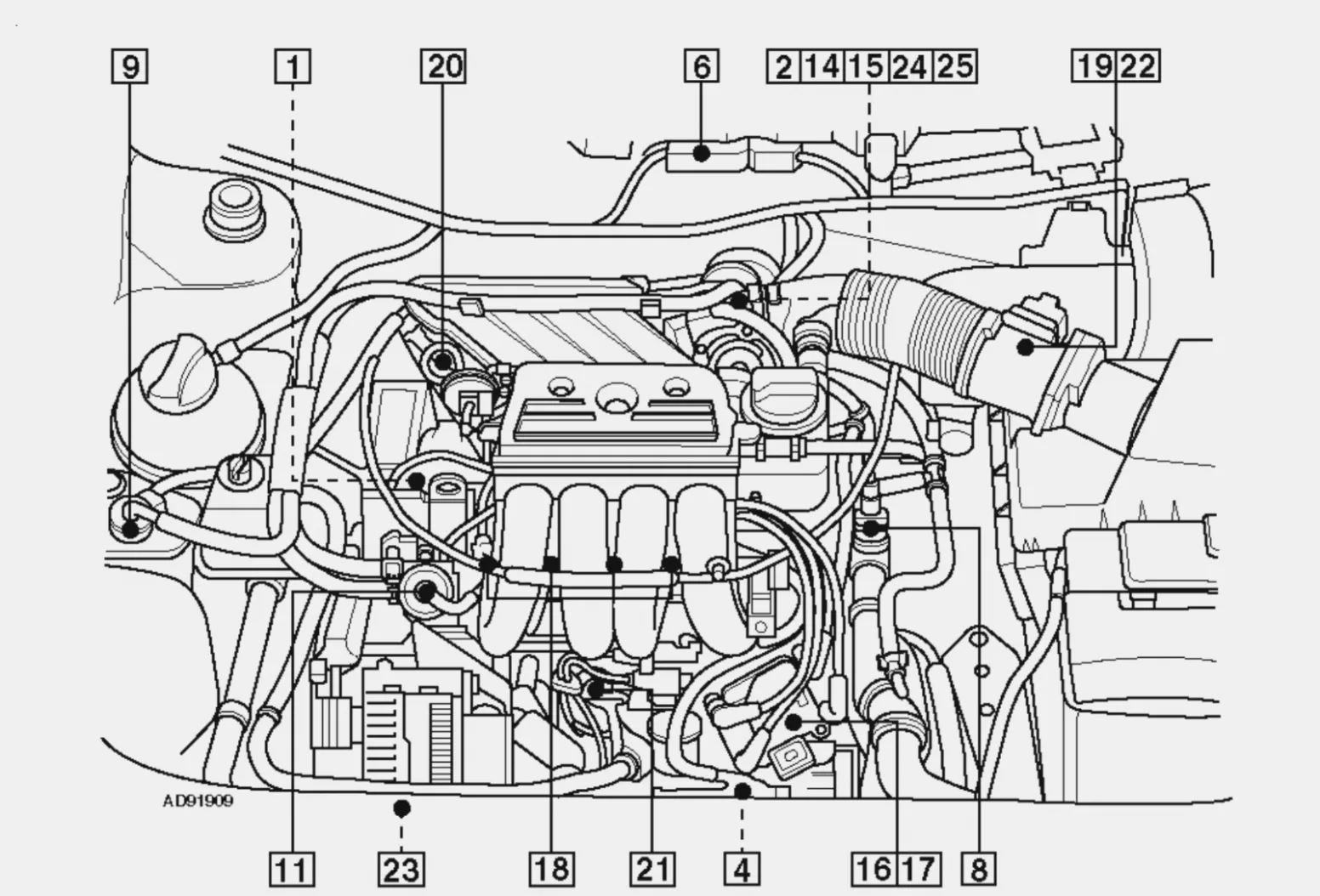
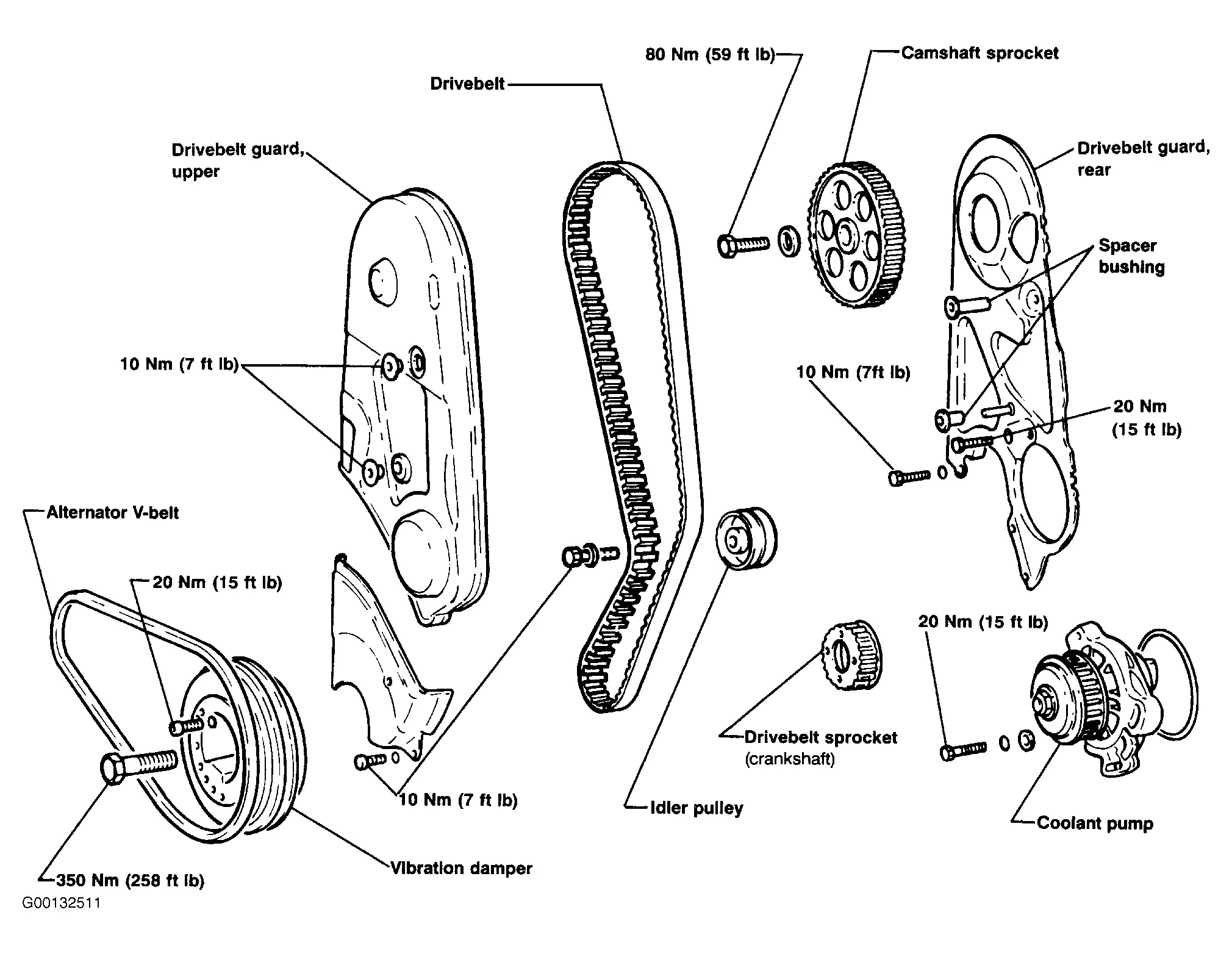
Vw Tdi Engine Belt Diagram Wallpapers
Related Images
More Images
Explore Topics 1
- Yamaha Kodiak 4510Wiring Diagram
- 2006 Durango Lighting Wiring Diagram
- Wiring Harness Diagram 2006 Chevy Cobalt
- 1991 Club Car Electrical Diagram
- Fuse Box Diagram For 2009
- Suzuki Eiger 4010Engine Diagram
- Peugeot Partner 2001 Wiring Diagram
- 1968 Dodge Coro Wiring Diagram
- 2004 Jeep Liberty Fuse Diagram
- 66 Mustang Heater Blower Wiring Diagram
Explore Topics 2
- 1991 Toyota Pickup Turn Signal Wiring Diagram
- Club Car Wiring Diagram 48V W Obc
- Falcon Boat Wiring Diagram
- Vw Jetta Horn Wiring Diagram
- Context Flow Diagram Bank Loan Management System
- 1979 Glastron Wiring Diagram
- 1969 Corvette Headlight Switch Wiring Diagram
- Enphase Wiring Diagram
- Pontiac Headlight Socket Wiring Diagram
- Beverage Airzer Wiring Diagram
Explore Topics 3
- 86 Ford F 1510Fuel Pump Relay Wiring Diagram
- Idec Relay Wiring Diagram Picture Schematic
- Dimension Audio Hyundai Car Wiring Diagram
- Cat 5 T568A Wiring Diagram Free Picture
- Eat Head Diagram
- 2002 Dodge Truck Wiring Diagram
- 2011Cadillac Srx Fuse Diagram
- 1989 Corvette Fuse Panel Diagram
- Traffic Lights Wiring Diagram
- Wiring Diagram For 74 Pinto
Explore Topics 4
- 20010Dodge Neon Side Mirror Wiring Diagram
- Headlight Wiring Diagram For 2005 Gmc Sierra
- Fuse Diagram 97 Chevy
- Bmw Door Diagram
- Grundfos Circulating Pump Wiring Diagram
- 48103 Phase Wiring Diagram
- 1979 Camaro Fuse Box Diagram
- 1997 Chevy Ignition Wiring Diagram
- Kenworth Fuse Panel Wiring Diagram
- Simplicity Regent Lawn Tractor Wiring Diagram
Explore Topics 5
- 4 Pin Wiring Diagram For Light Reading
- Simplehuman Ear Diagram
- Wiring Diagram Honda D
- 1998 Jeep Cherokee Sport Fuse Box Diagram
- 3 Phase Wye Wiring Diagram
- 1996 Dodge Ram 25010Trailer Wiring Diagram
- Dodge Magnum Parts Diagram
- Simple Car Diagram
- 2008 Mazda 6 User Wiring Diagram
- Volvo C310User Wiring Diagram