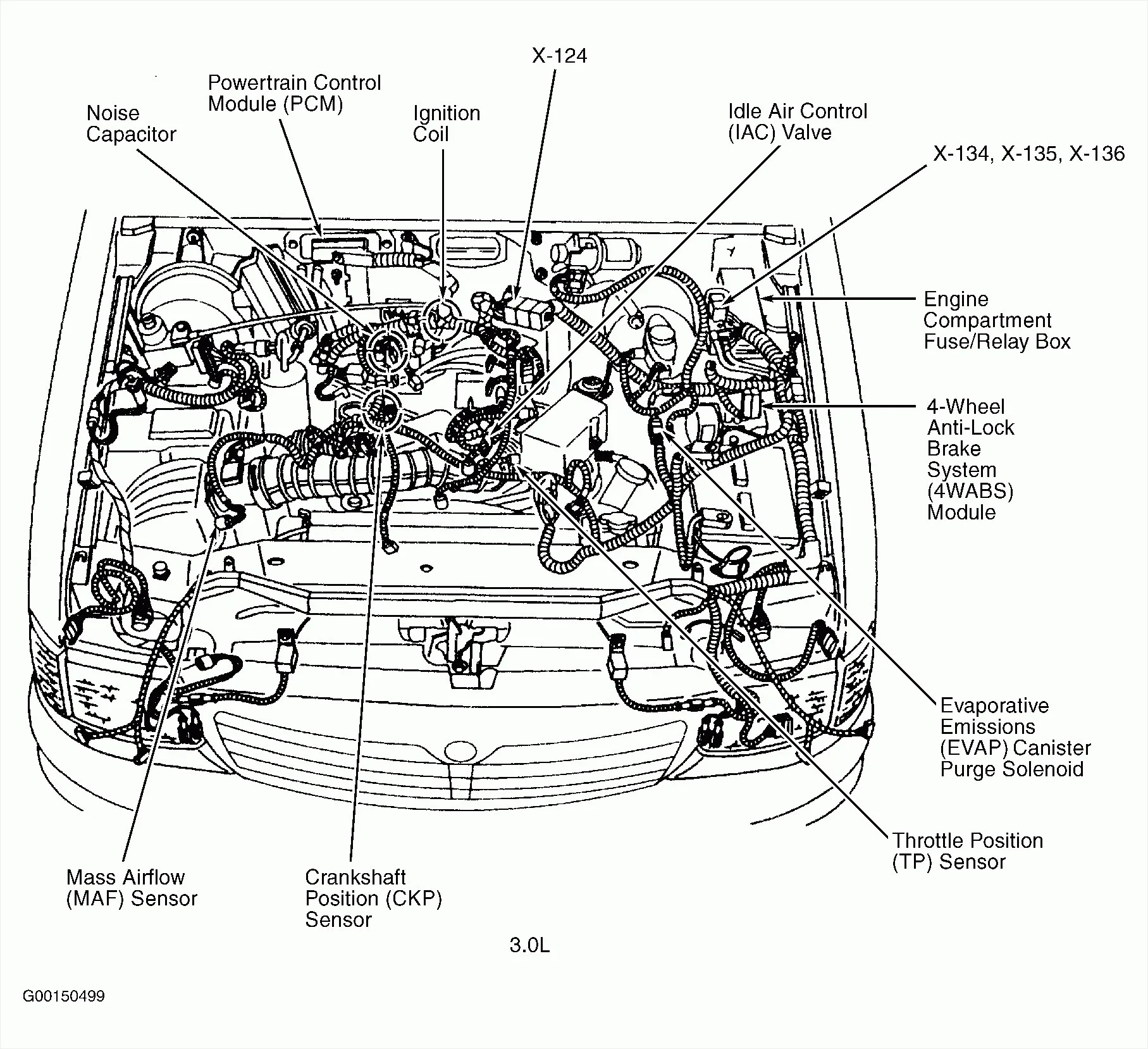
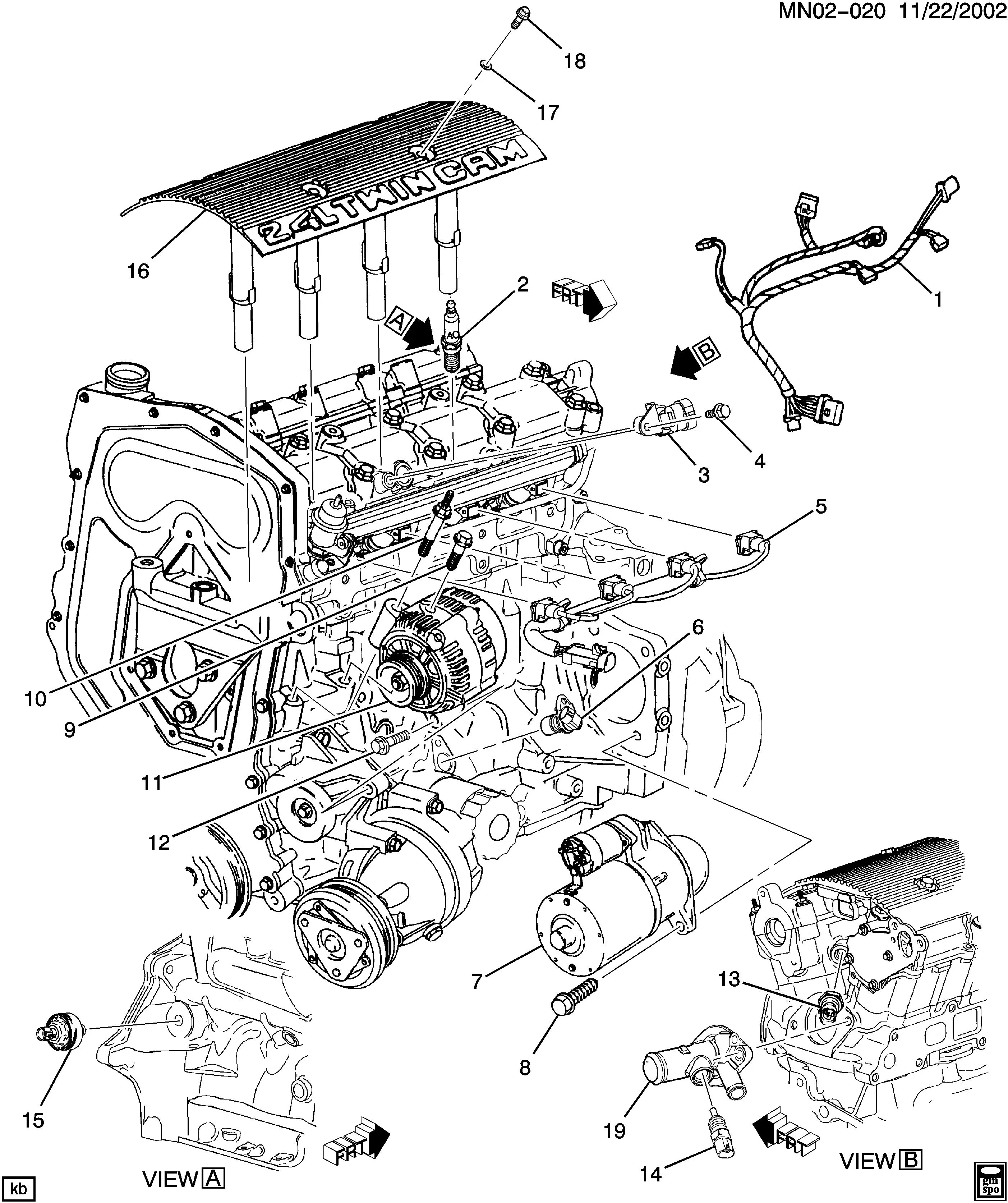
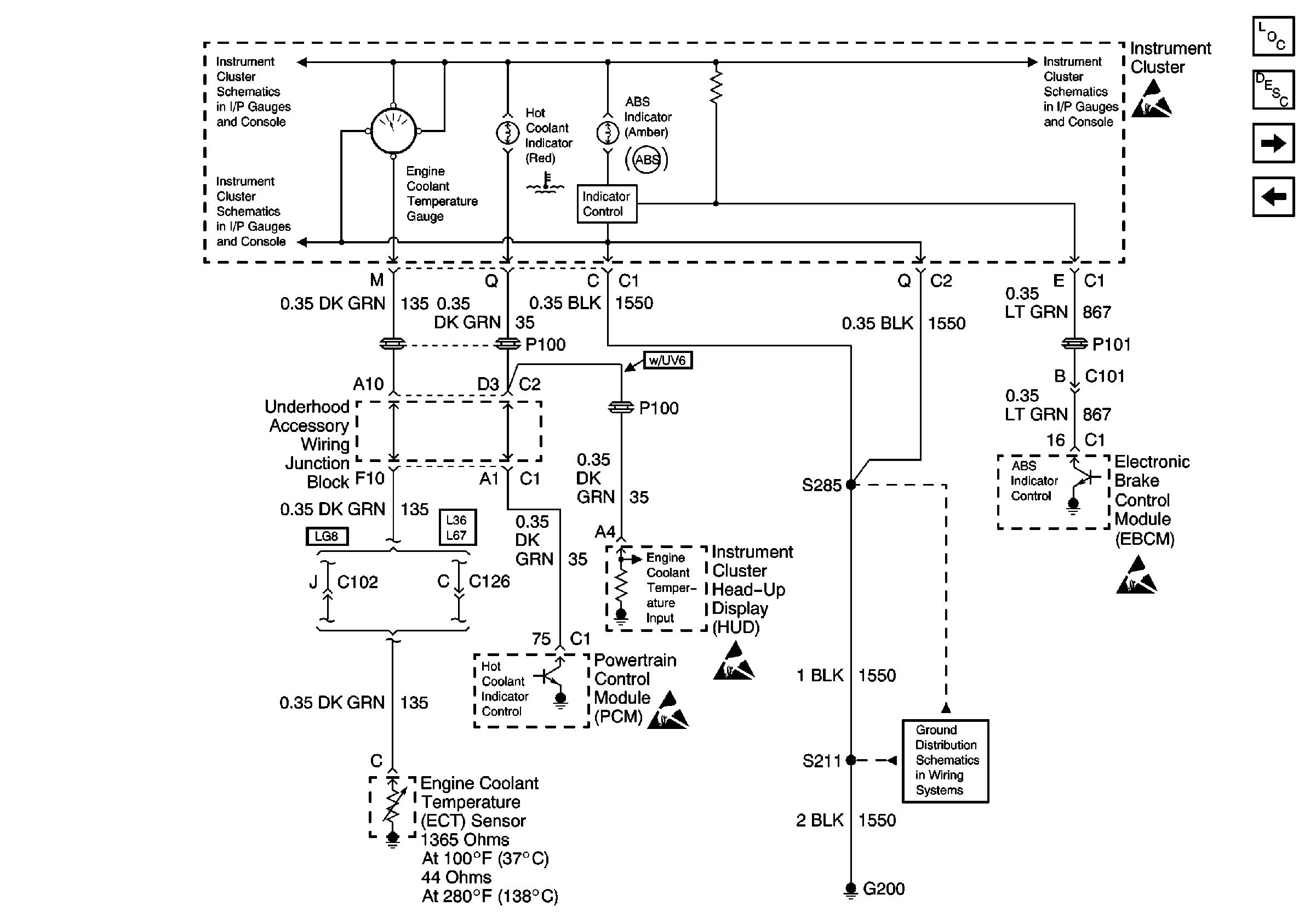
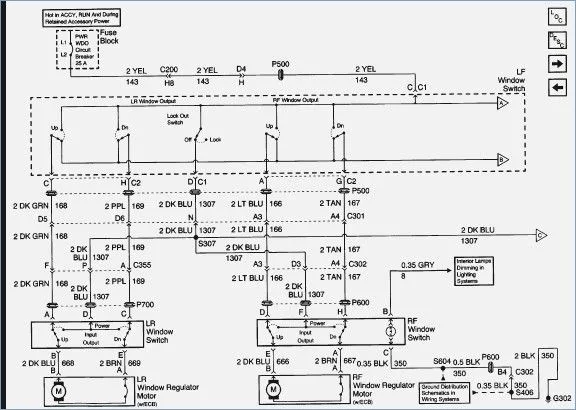
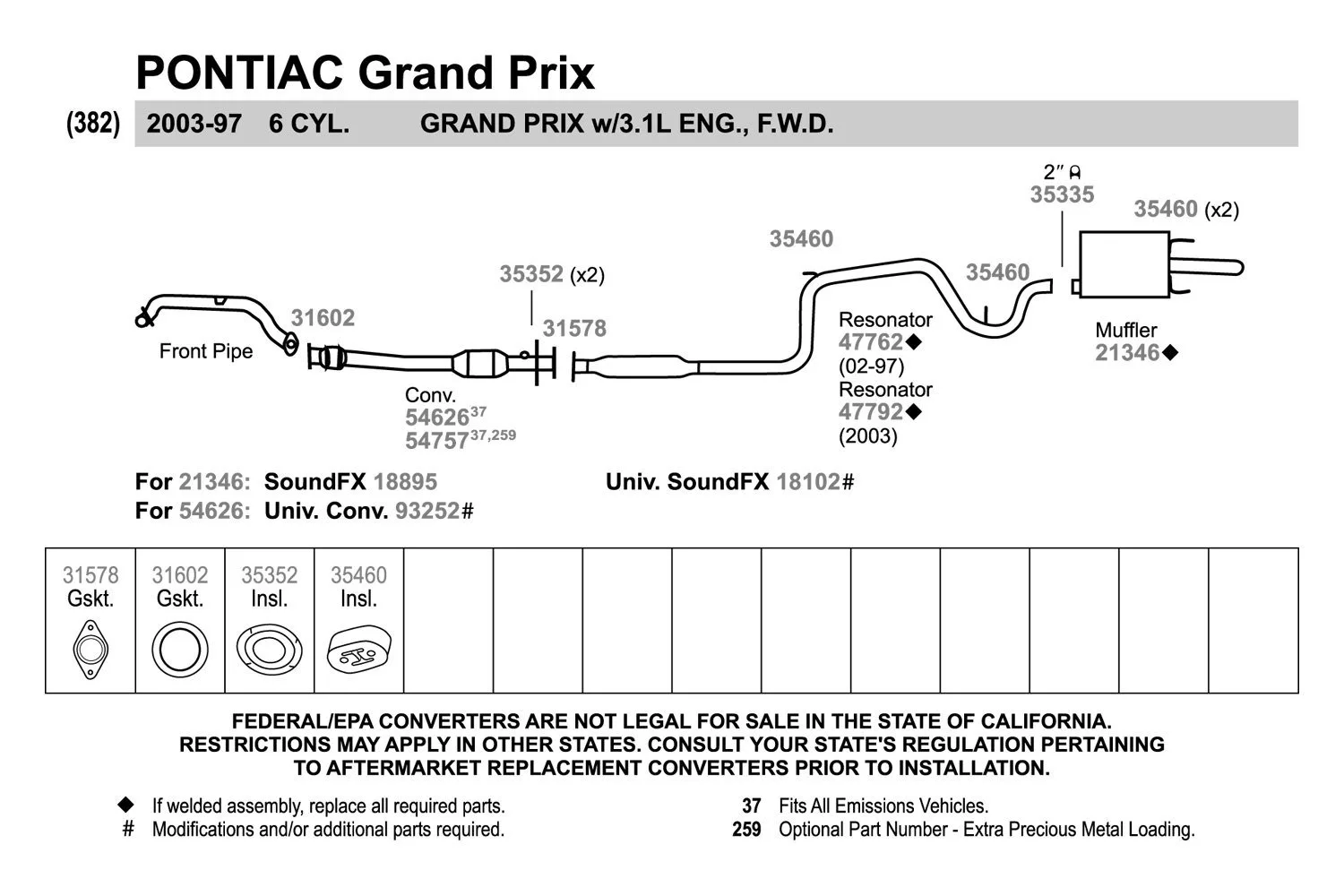
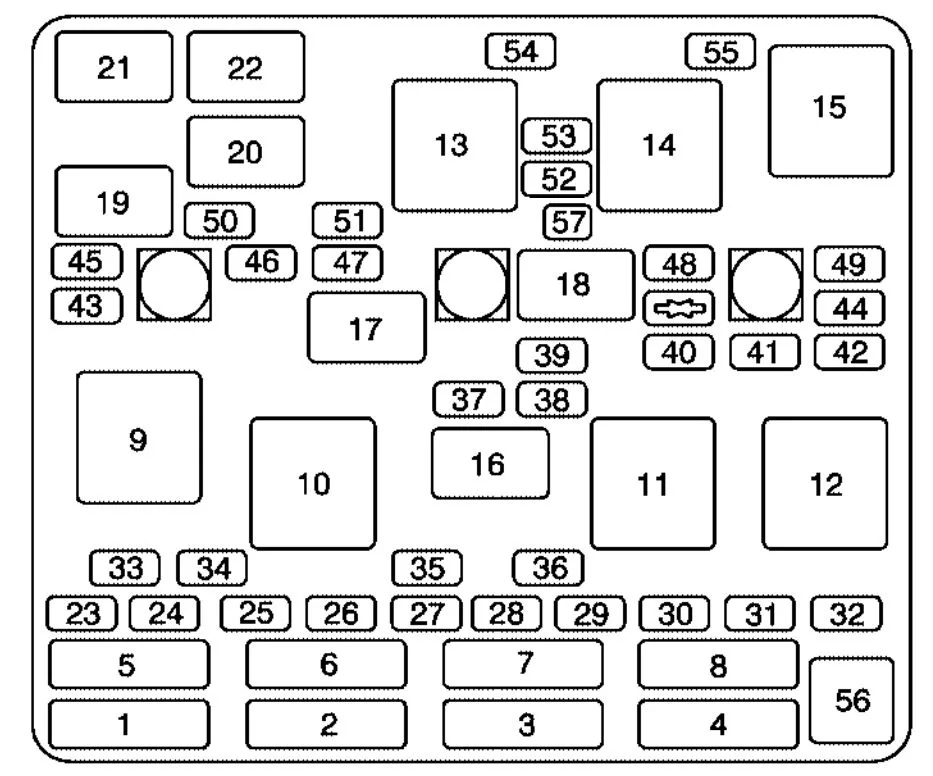
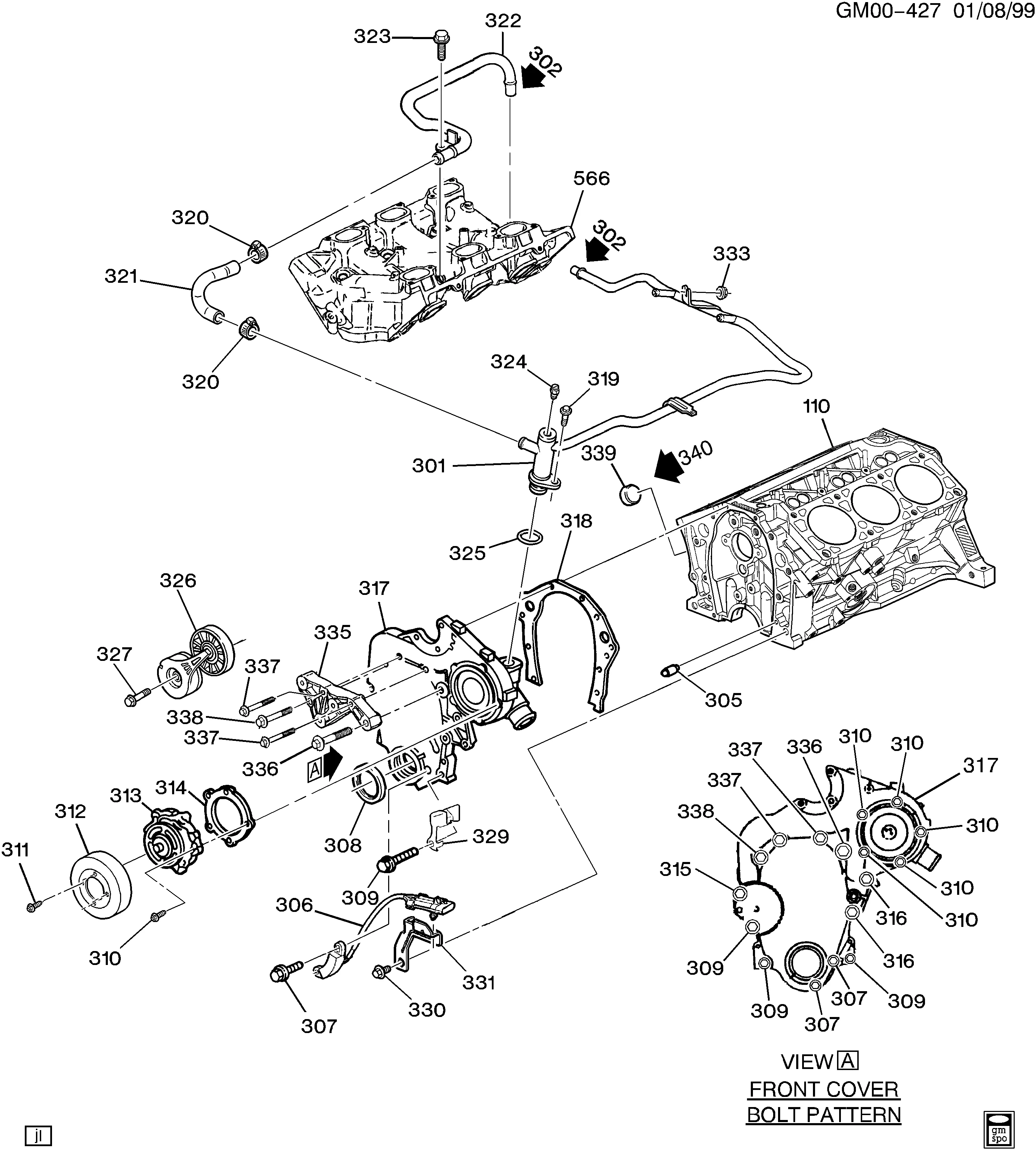
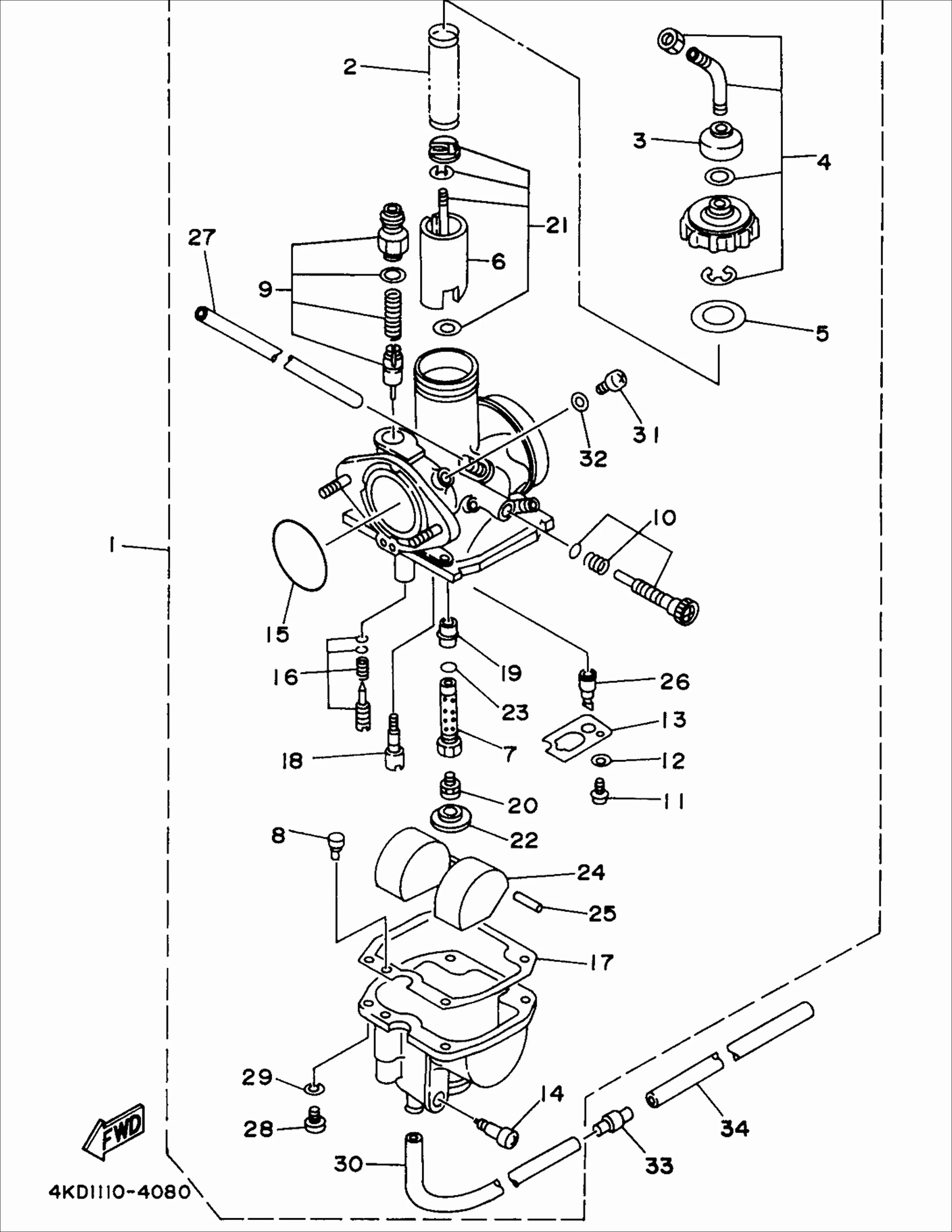
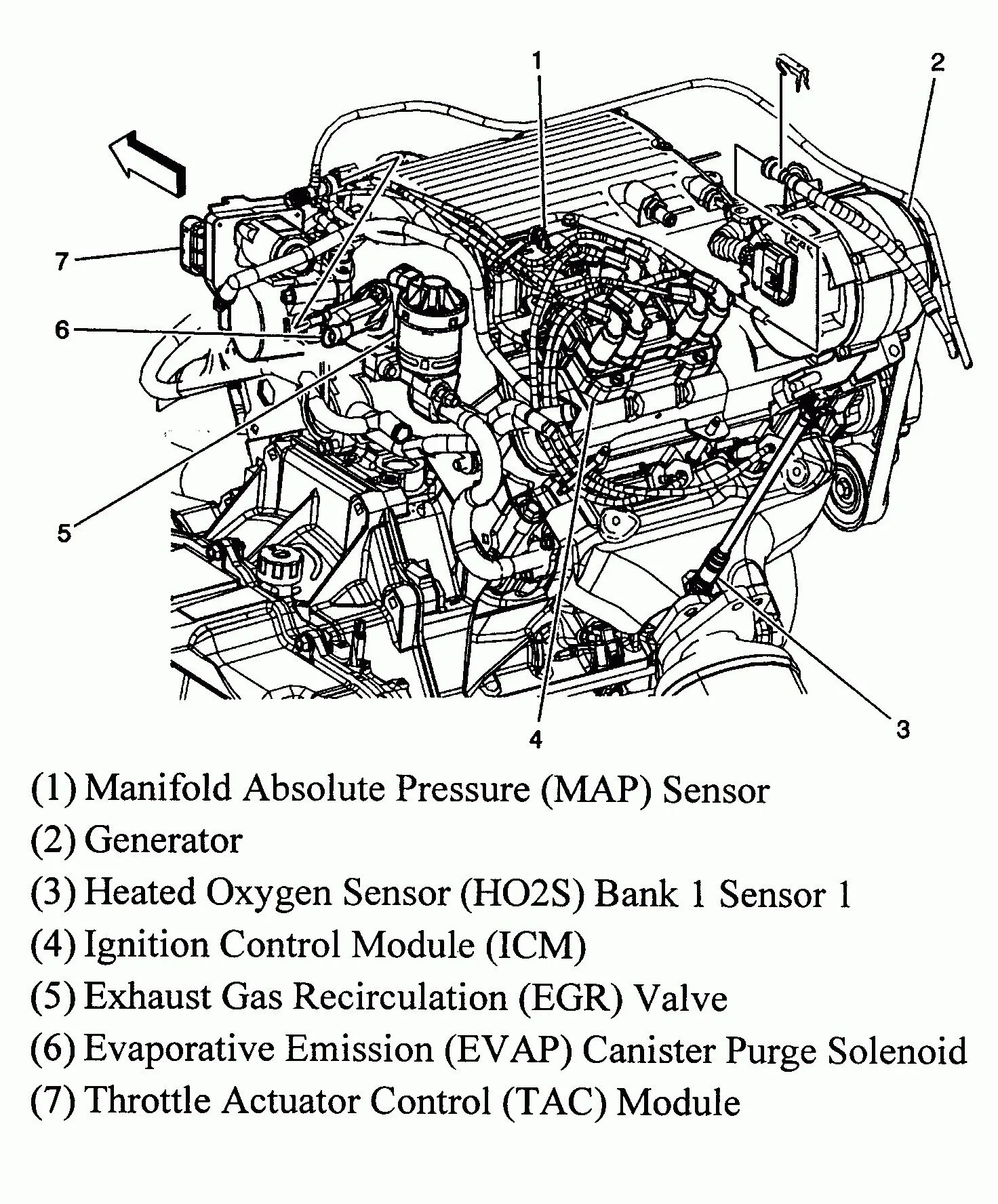
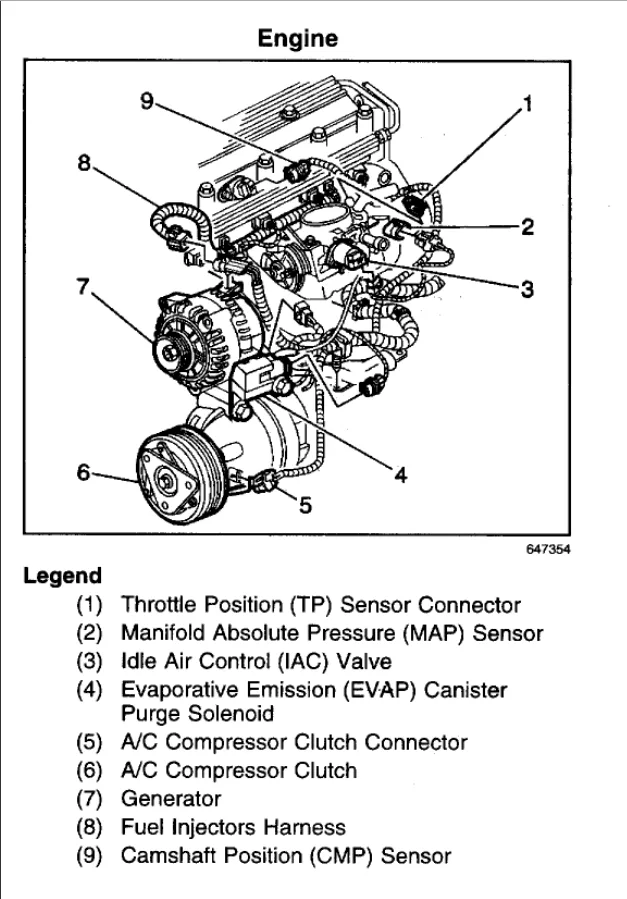
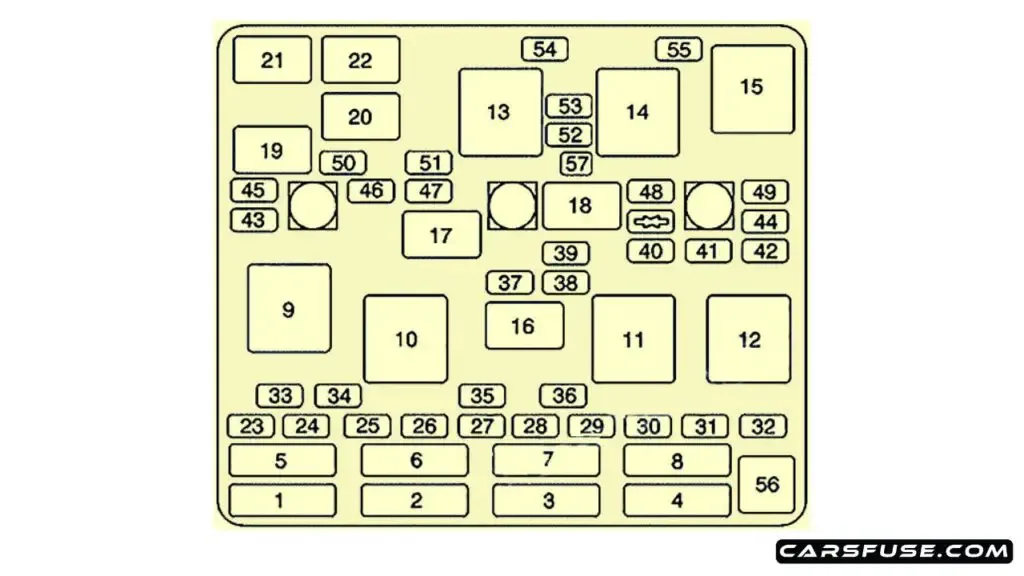
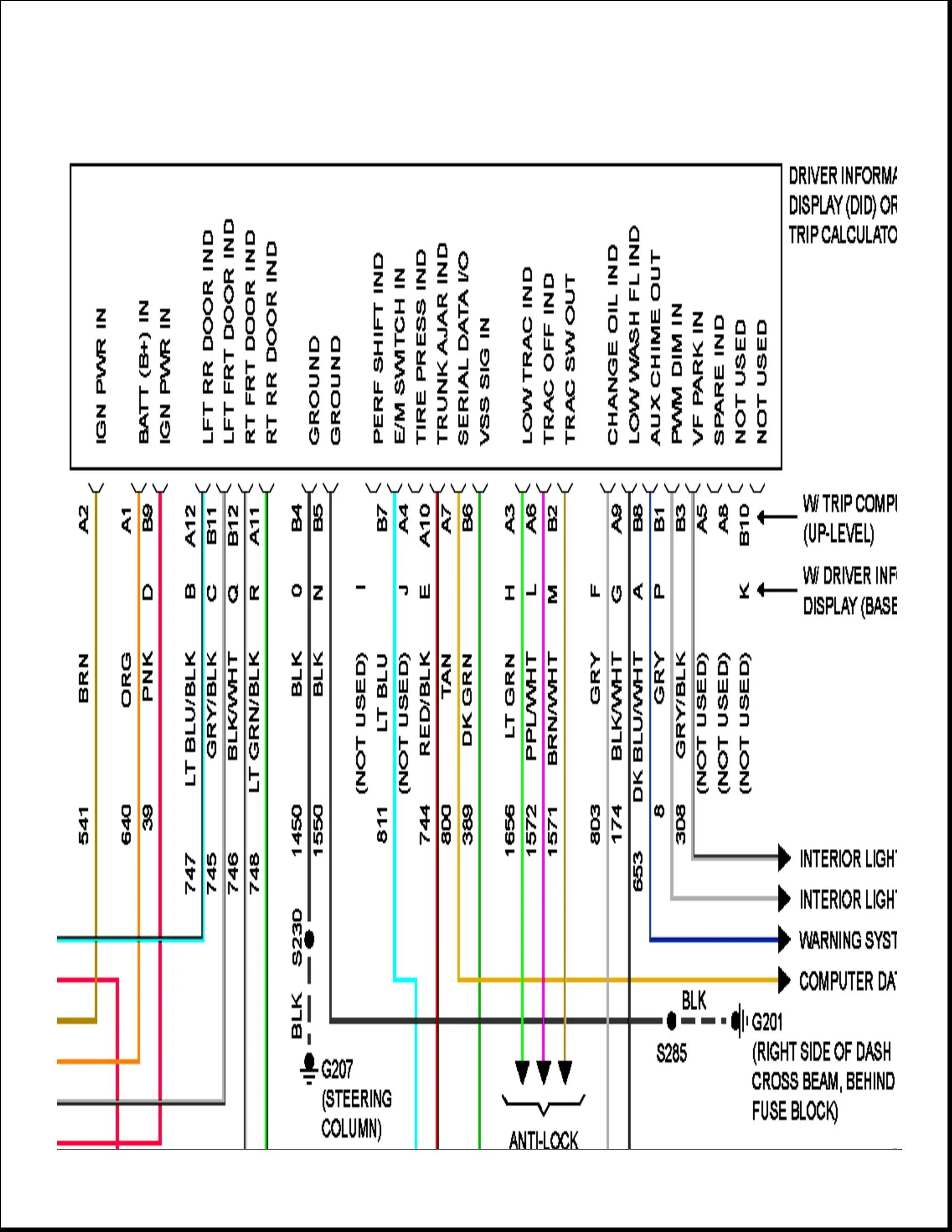
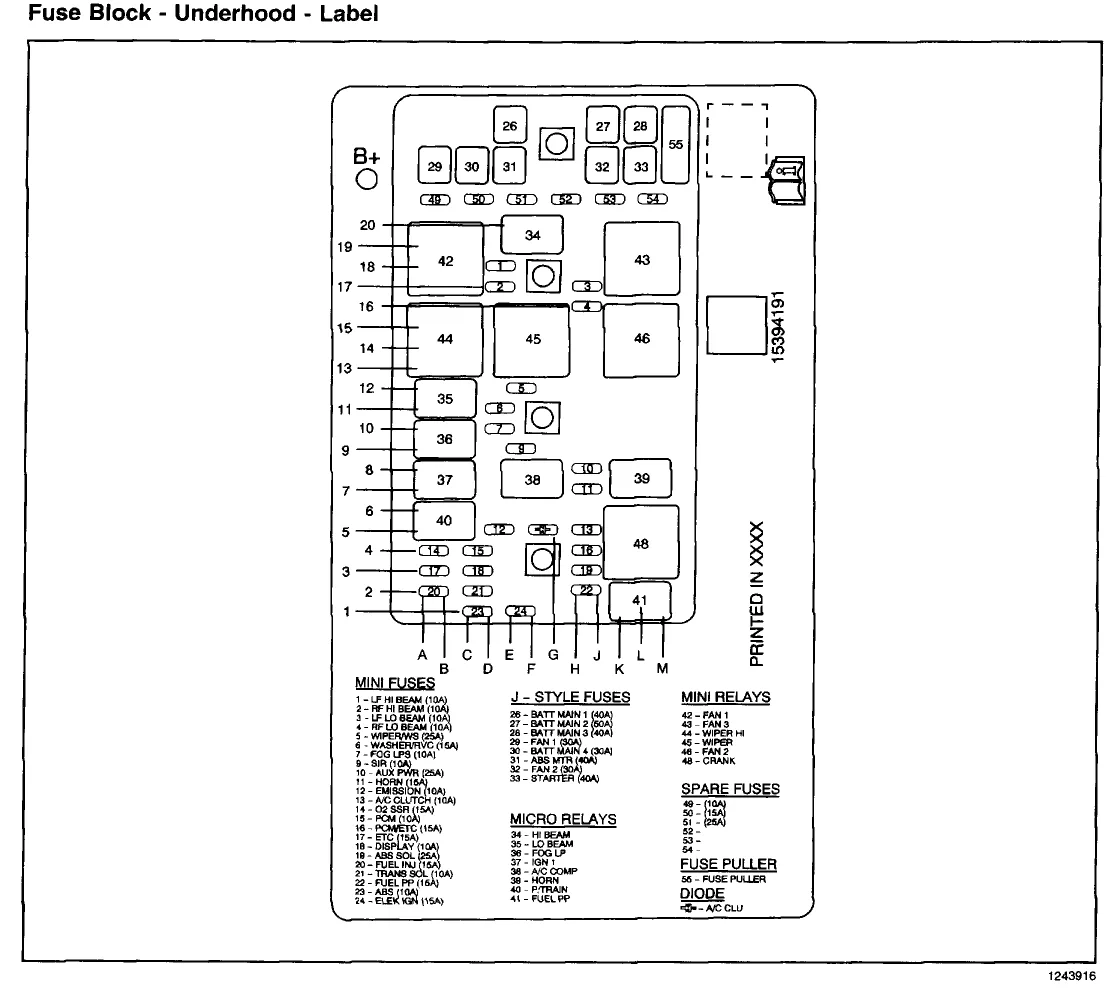
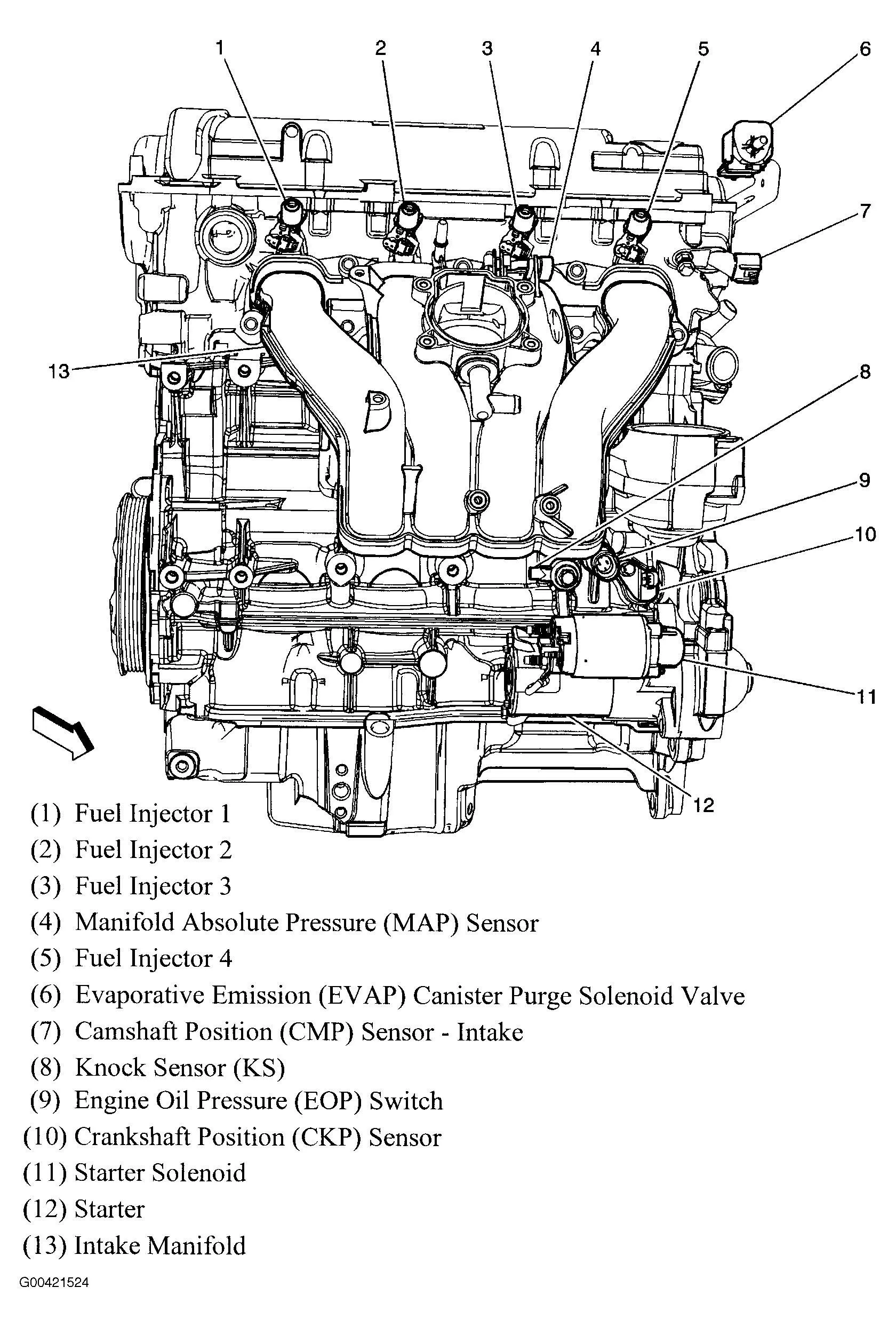
Pontiac Grand Am Engine Diagram Wallpapers
Related Images
More Images
Explore Topics 1
- Peugeot 206 Cc Haynes Wiring Diagram
- Simon Xt Alarm System Wiring Diagram
- Canned Light Switch Wiring Diagram
- Alfa Romeo 156 Jtd Wiring Diagram
- 2006 Altima Engine Fuse Box Diagram
- Ruud Compressor Wiring Diagram
- Humbucker Wiring Diagram
- Fuse Diagram For 2013 Ford Focus
- 2001 F1510Trailer Wiring Diagram
- Small Engine Valve Tap Pet Diagram
Explore Topics 2
- Dual Car Audio Wiring Harness Diagram Xd5125
- Yanmar 165 Wiring Diagram
- Chev 305 Hei Distributor Wiring Diagram
- Chevrolet Hhr Engine Diagram
- 2005 Suburban Fuse Diagram
- Ford Taurus 2001 Fuse Box Diagram
- Holden Astra Electric Power Steering Pump Wiring Diagram
- Evap Cooler Wiring Diagram
- Infiniti Stereo Wiring Diagram
- Craftsman Gt50010Deck Wiring Diagrams
Explore Topics 3
- House Wiring Diagram Switch
- Volvo Sensus Wiring Diagram
- 3 Wire Zone Valve Diagram
- Keelboat Diagram
- 1988 Toyota Camry All Trac Service Repair Set 88 Service Electrical Wiring Diagrams And The Air Conditioner Installation
- 2006 Saturn Ion Blower Motor Wiring Diagram
- Hyundai O2 Sensor Wiring Diagram
- 94 Buick Roadmaster Fuse Box Diagram
- Circline Wiring Diagram
- Kicker Ck8 Wiring Diagram
Explore Topics 4
- 20110Saab 9 5 Wiring Diagram
- Colored Ct710Wiring Diagram
- 87 Cougar Wiring Diagram
- Impala Power Seats Wiring Diagram
- Atc Engine Diagram
- Wiring Diagram For Bosch O2 Sensor
- 2004 Kia Amanti Fuse Diagram
- Ge Refrigerator Wiring Circuit Diagram
- Ricoh Aficio Mp25510335102851 3351 Service Parts Diagram
- 1979 Ford Wiring Diagram
Explore Topics 5
- Toyota Abs Relay Wire Diagram
- Honda Rebel 5010Wiring Diagram
- 1949 International Cub Wiring Diagram
- 150Cc Atv Wiring Diagram
- 2003 Chevrolet 35010Fuse Box Diagram
- Uconnect Radios Wiring Diagrams
- Stamford Alternator Wiring Diagrams Pdf
- 1989 Chevy Silverado Ignition Wiring Diagram
- 2015 Toyota V6 Engine Diagram
- 1992 22Re Wiring Harness Diagram